Advertisement
U.S. at Risk of Not Reaching 90 Percent Graduation Rate Goal by 2020
By Jason Owen
7 min read
Advertisement - Continue reading below
WASHINGTON, May 3, 2017 /PRNewswire-USNewswire/ — Since 2001, 2.8 million more students have graduated from high school rather than dropping out. In an economy that prizes educational attainment more than ever before, these rising rates have created enormous benefits for individuals, communities and our entire nation. But even now with the current national graduation rate at 83.2 percent, it is becoming more evident that the nation will be unable to meet its high school graduation rate goal without intensifying efforts to reach the students who have historically faced the greatest challenges. The country remains off-pace to reaching its goal for the second year in a row.
Today, Civic Enterprises and the Everyone Graduates Center at the Johns Hopkins University, in partnership with America’s Promise Alliance and the Alliance for Excellent Education, released the 2017 Building a Grad Nation report, the eighth annual update on the progress and challenges in raising high school graduation rates. The four organizations lead the GradNation campaign, a nationwide effort to boost on-time high school graduation rates to 90 percent by the Class of 2020. The 2017 report is presented by lead sponsor AT&T and supporting sponsor State Farm.
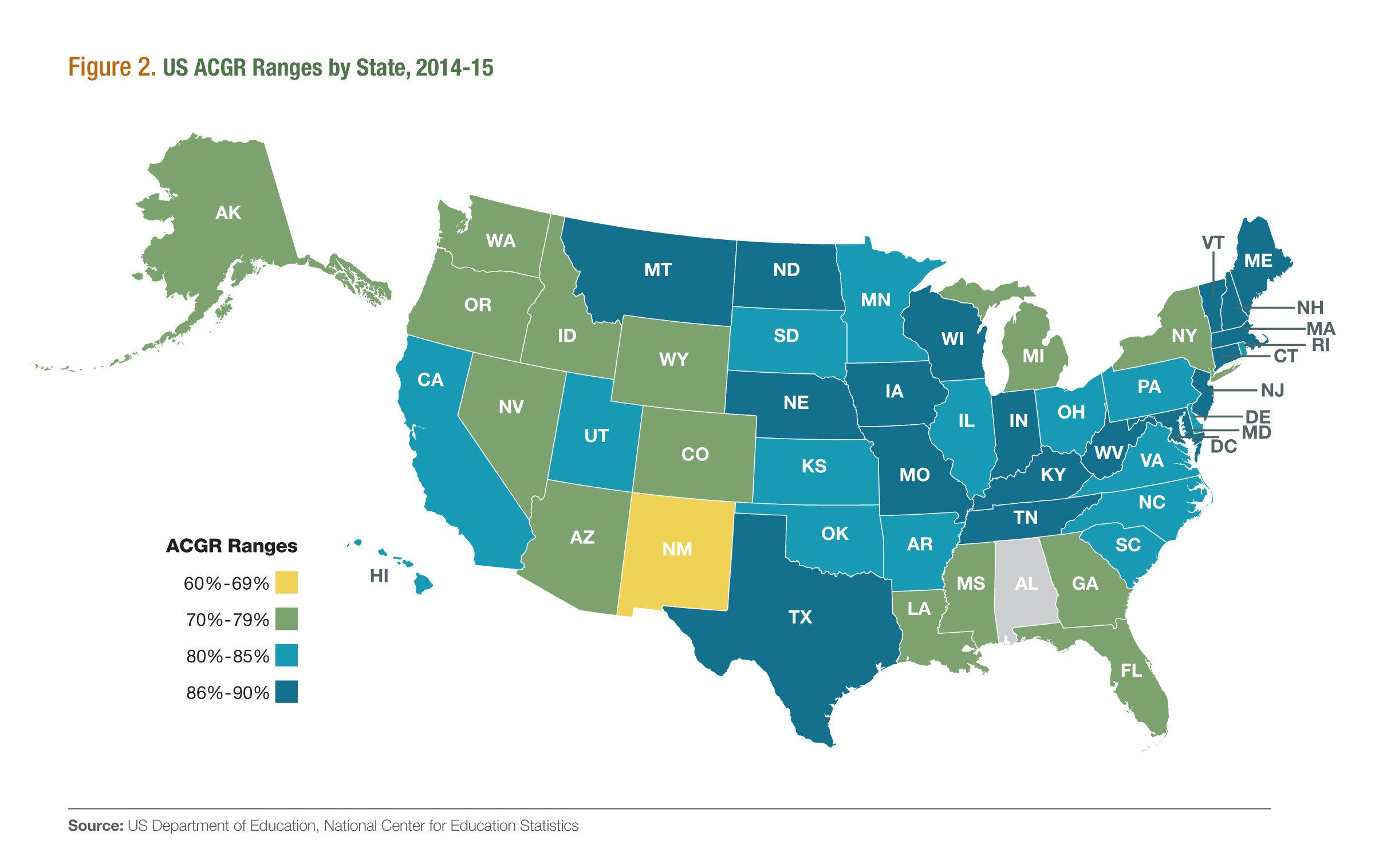
This year’s report marks five years since states have used the Adjusted Cohort Graduation Rate (ACGR), a common formula for collecting graduation statistics across states, and among a variety of subgroups. With just five years of federal data remaining until 2020, the data also make it clear that the rate of progress must increase significantly if the country is to reach its goals. Only half of America’s states are on track to reach a 90 percent graduation rate by 2020.
“National high school graduation rates increased four percentage points from 2010 to 2015. That’s more than just a data point – it means hundreds of thousands more young people are in a better position for post-secondary enrollment. These increases, reflected across all states and student subgroups during that five-year period, are a profound achievement for our nation,” said Robert Balfanz, director of the Everyone Graduates Center at the Johns Hopkins University School of Education and co-author of the report. “Now, as we move into the last leg of the campaign, we must double our progress if we are to meet our goal. This report offers a blueprint for how to get there.”
“In 2015, about half of the country reported high school graduation rates of 85 percent or higher, putting more states on track to reach a 90 percent graduation rate by 2020,” said John Bridgeland, president & CEO of Civic Enterprises and co-author of the report. “But our country must do more to achieve equity across state lines. It’s time to sharpen our focus on the hardest to reach populations and work to elevate them to success.”
Skepticism Over the Authenticity of Graduation Gains. Rising rates have been met with heightened scrutiny. Issues range from the collection and reporting of data, the increase in the number of alternative schools with lower graduation standards, multiple high school diplomas with varying standards of excellence and the question of whether increasing high school graduation rates are actually translating into gains in post-secondary enrollment and attainment. These pockets of concern for specific states or particular types of schools are cause for careful review. But the data also show that these challenges do not outweigh the rising national trend.
“More must be done to curtail errors in data collection, states and school districts must continue be held accountable for the students in their care, and a watchful eye must be kept on alternative high school programs that are often working with the most disadvantaged students,” said Jennifer DePaoli, senior research and policy advisor at Civic Enterprises and co-author of the report. “This year’s report should drive key stakeholders to renew their commitments and invest in best practices to improve educational outcomes for the most marginalized student groups.”
Key Findings. The Building a Grad Nation report is based on the most recent comprehensive data from the National Center for Education Statistics at the U.S. Department of Education (2014-15). A close look at the data shows disparities in graduation rates in five key areas.
- Low-income students: Nearly half of the country’s 2015 graduating cohort – 48.2 percent, a slight increase from 2014 – came from low-income families. Nationally, the gap between low-income students and their middle- and upper-income peers now stands at 13.7 percentage points. In nearly half of all states, the gap between low-income students and their more affluent peers is 15 percentage points or greater, and in 18 additional states the gap is at least 10 points.
- Black and Hispanic/Latino Students: Graduation rates for Black students have increased 7.6 percentage points and 6.8 percentage points for Hispanic/Latino students since 2011 – some of the highest gains of any student subgroup. However, Black and Hispanic/Latino students comprise 54 percent of all students who did not graduate on time.
- Students with disabilities: Thirty-three states reported high school graduation rates for special education students below 70 percent, and nearly half of those 33 states had graduation rates for students with disabilities below 60 percent. Four states – South Carolina, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Nevada – graduated less than half of their special education students. Nationally, the graduation rate gap between students with and without disabilities now stands at 21.1 percentage points. In 29 states, students in the general education population graduate at rates of 20 percentage points or more than their special education peers.
- English Language Learners: The number of ELL students in America’s public schools is climbing, increasing from 8.8 percent (an estimated 4.2 million students) in 2003-04 to 9.2 percent (an estimated 4.5 million) in 2013-14. The 10 states with the highest proportion of ELL non-graduates comprised 66 percent of all ELL non-graduates in the country, while over one-third of English Language Learners who did not graduate on time are located in California alone.
- Low-Graduation-Rate High Schools: Since 2002, the number of large, low-graduation-rate high schools (enrolling 300 or more students) has been cut in half and there are now fewer than 900,000 students enrolled in them – down from 2.5 million. There were 2,249 low-graduation-rate high schools (enrolling 100 or more students) in 2015, making up just 12 percent of all public high schools enrolling 100 or more students. Two out of three students in low-graduation-rate high schools are Black or Hispanic/Latino. Six in ten students in low-graduation-rate high schools qualified as being low-income in 2015, meaning that there is little economic diversity in the nation’s most challenged high schools.
Policy recommendations. The report recommends policymakers: 1) Create high-quality Every Student Succeeds Act implementation plans; 2) Create evidence-based plans to improve low-graduation-rate high schools; 3) Get the cohort rate right by improving uniformity and transparency in the ACGR; 4) Report extended-year graduation rates; and 5) Strengthen accountability for non-traditional high schools.
In a recent letter to the U.S. Department of Education, GradNation campaign leaders offered some of these same recommendations in the wake of the recent repeal of ESSA regulations by Congress.
“Graduation rate progress is primarily a state and local responsibility, but federal oversight remains a critical component of making sure that traditionally underserved students receive the support they need,” said Bob Wise, president of the Alliance for Excellent Education and former governor of West Virginia. “By implementing and supporting policies that strengthen accountability and transparency, we avoid potential loopholes that can be devastating to many young people.”
The Road to 90. The 2014-15 school year marks the second year that the country is not on track to reach its goal. To stay on track, the national graduation rate must increase by 1.4 percentage points annually. For 2015, the rate went up just 0.9 percent.
“We need a real breakthrough on equity if we are going to get more young people across the graduation stage over these next few years,” said John Gomperts, president and CEO of America’s Promise Alliance. “To help accelerate progress, the campaign going forward will focus more on supporting targeted strategic statewide and local plans that will work toward leveling the playing field and moving the needle to help more young people and schools succeed.”
Authors and sponsors. The 2017 Building a Grad Nation report is co-authored by Jennifer DePaoli, John Bridgeland, Erin Ingram and Matthew Atwell of Civic Enterprises and Robert Balfanz and his team at the Everyone Graduates Center at the Johns Hopkins University School of Education. AT&T, lead sponsor, has supported the Building a Grad Nation report series through AT&T Aspire, the company’s $400 million commitment since 2008 to graduate more students from high school ready for college and career. State Farm is a supporting sponsor.
Full report. To read the full report, access graphics, state-by-state data and other resources, visit: www.gradnation.americaspromise.org/report/2017-building-grad-nation-report.
Join the Livestream. A livestream of the Building a Grad Nation report release event will be available on May 3 from 3-4:30 PM ET. The event will showcase the release of research by Civic Enterprises and The Everyone Graduates Center, followed by a moderated panel conversation to address the key challenges associated with raising graduation rates, featuring voices from leaders on the ground and researchers in the field. Join the conversation here: http://www.americaspromise.org/event/state-our-gradnation-what-will-it-take-get-90-percent-grad-rate-all-students.
Civic Enterprises is a public policy and strategy firm that helps corporations, nonprofits, foundations, universities and governments develop and spearhead innovative public policies to strengthen our communities and country. Created to enlist the private, public and nonprofit sectors to help address our nation’s toughest problems, Civic Enterprises fashions new initiatives and strategies that achieve measurable results in the fields of education, civic engagement, economic mobility, and many other domestic policy issues. www.civicenterprises.net
The Everyone Graduates Center at the Center for Social Organization of Schools at the School of Education at Johns Hopkins University seeks to identify the barriers to high school graduation, develop strategic solutions to overcoming these barriers and build local capacity to implement and sustain the solutions so that all students graduate prepared for adult success. www.every1graduates.org
America’s Promise Alliance leads the nation’s largest network dedicated to improving the lives of children and youth. As its signature effort, the GradNation campaign mobilizes Americans to increase the on-time high school graduation rate to 90 percent by the Class of 2020 and prepare young people for postsecondary enrollment and the 21st century workforce. www.AmericasPromise.org
The Alliance for Excellent Education is a Washington, DC-based national policy and advocacy organization dedicated to ensuring that all students, particularly those who are traditionally underserved, graduate from high school ready for success in college, work, and citizenship. www.all4ed.org
SOURCE GradNation Campaign
Advertisement - Continue reading below